The human body orchestrates a complex symphony of immune responses, employing an ensemble of innate immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells as the first line of defense against microbial invaders and parasites. This intricate defense system is governed by a sophisticated network of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), with Toll-like receptors, C-type lectin receptors, NOD leucine-rich-repeat containing receptors, and RIG-1 helicase receptors playing pivotal roles. In this symphony, the cytokine IL-15 emerges as a key conductor, influencing the development, differentiation, and survival of various innate immune cells.
IL-15 Expression: Linchpin in Immune Regulation
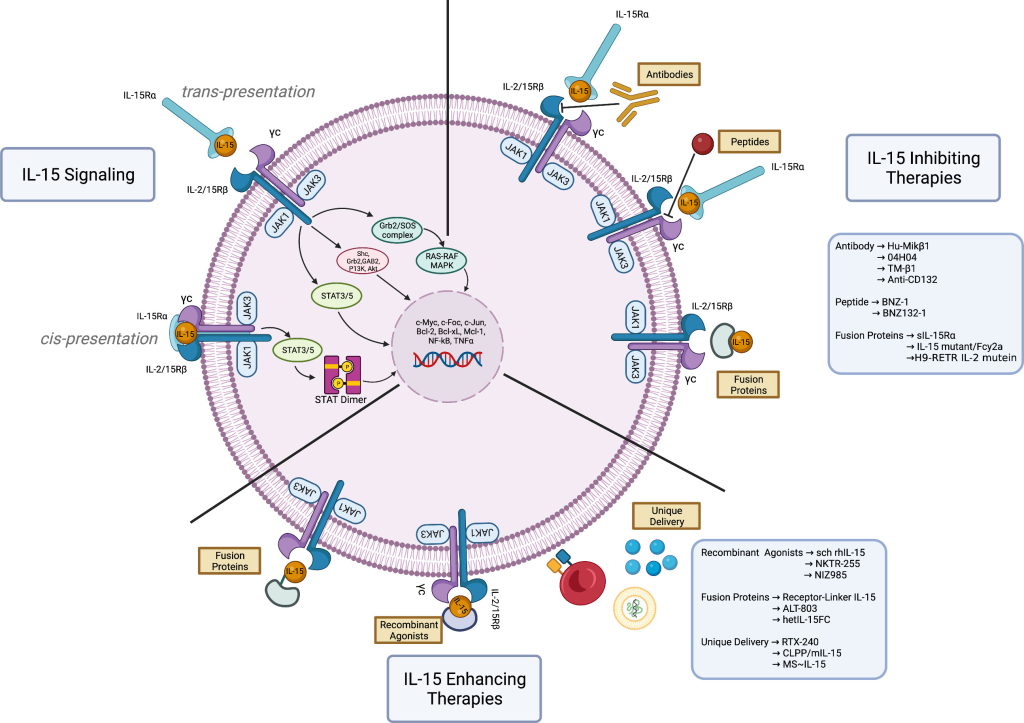
Mature IL-15, a 14–15 kDa glycoprotein, is a keystone in immune regulation. Its expression is tightly controlled through transcription, translation, translocation, and intracellular trafficking. Various cell types express IL-15 mRNA, but few secrete detectable IL-15 proteins, owing to structural intricacies like multiple AUG initiation sites and alternative splicing. Interestingly, the secretion of IL-15 involves a unique transport mechanism termed trans-presentation, where IL-15 is transported through the Golgi apparatus bound to IL-15 receptor α (IL-15Rα). This molecular ballet raises questions about species-specific differences in IL-15 delivery and responses.
IL-15 Signaling: A Molecular Pas de Deux
IL-15 orchestrates its effects by binding to IL-15Rα and signaling through a β chain and a γ chain complex. This prompts the recruitment of Janus kinase (JAK) JAK1 and the activation of JAK3, leading to the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins STAT3 and STAT5. The shared signaling complex with IL-2 positions IL-15 as a unique player with immunomodulatory properties, distinct from IL-2. This intricate dance of cytokine signaling not only shapes the immune responses of T lymphocytes but also extends to various other cell types and tissues, contributing to the systemic effects seen with IL-15.
IL-15 on Innate Immune Cells: Cellular Ballet at the Front Lines
NK Cells: Guardians of Viral Frontiers
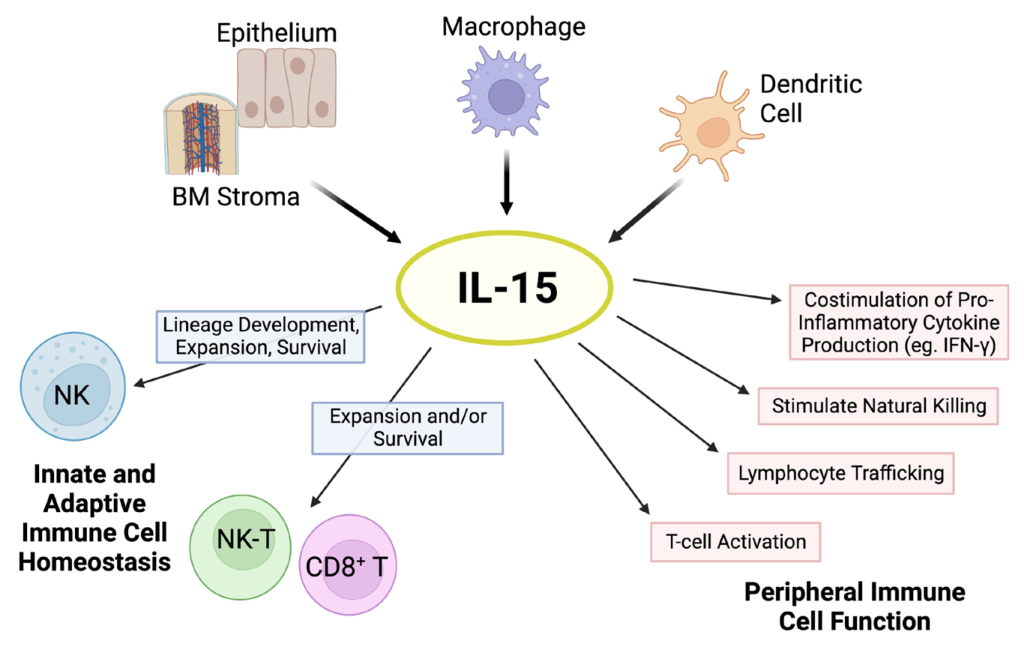
Natural Killer (NK) cells, pivotal in immune defense against viruses, bacteria, and tumors, depend critically on IL-15 for development and survival. Despite not producing IL-15, resting NK cells express IL-15Rα, relying on trans-presented IL-15 by CD11c+ dendritic cells for their maintenance. IL-15’s influence extends to the differentiation of CD56+ NK cells from hematopoietic progenitor cells and modulating their cytotoxicity and cytokine production. Understanding the impact of IL-15/IL-15Rα complexes on NK cell function provides insights into manipulating these cells for therapeutic purposes.
Monocytes/Macrophages and DCs: Architects of Adaptive Immune Responses
Circulating monocytes, evolving into macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs), emerge as crucial architects shaping adaptive immune responses. IL-15’s impact on these cells ranges from inducing proinflammatory cytokine production to modulating the adaptive immune response through the regulation of IL-2 production by DCs. Moreover, IL-15 contributes to the survival of DCs, highlighting its multifaceted role in immune regulation.
Neutrophils and Eosinophils: Swift Footwork in Inflammation
Neutrophils, the rapid responders at inflammatory sites, express IL-15Rα and exhibit diverse responses to IL-15, from cytoskeletal rearrangement to increased phagocytosis and delayed apoptosis. IL-15’s influence on neutrophils extends to enhancing their antimicrobial functions, promoting migration, and augmenting their ability to respond to infections. Similarly, eosinophils display an intricate dance under IL-15’s influence, contributing to the orchestrated inflammatory response.
Mast Cells: Guardians at the Interfaces
Strategically located at the host’s interfaces with the environment, mast cells play a crucial role in protecting against various infections. IL-15, signaling through an alternative receptor (IL-15TX), regulates mast cell proliferation, survival, and migration. Understanding how IL-15 controls mast cell function sheds light on the intricate interplay between the immune system and pathogens.
Other Innate Immune Cells: The Symphony Ensemble
IL-15’s influence extends beyond NK cells and macrophages to unique lymphocyte subsets like NK1.1 T cells and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). The development and proliferation of these cell types are intricately linked to IL-15, highlighting its role as a master regulator in the symphony of innate immune responses.
Deciphering IL-15’s Role in Shaping Adaptive Immune Cell Dynamics
IL-15 and CD8+ T Lymphocytes: Orchestrating Memory and Survival
IL-15 emerges as a linchpin for the survival and maintenance of memory CD8+ T lymphocytes. Experiments with IL-15- and IL-15Rα-deficient mouse strains underscore its critical importance, revealing a stark reduction in memory CD8+ T lymphocytes. Further investigations shed light on IL-15’s role in upregulating anti-apoptotic molecules, specifically Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, ensuring the persistence of these vital immune sentinels. Despite conflicting observations regarding its necessity in primary CD8+ T lymphocyte expansion, IL-15 indisputably plays a pivotal role in basal homeostatic proliferation of memory CD8+ T lymphocytes.
IL-15’s Influence on CD4+ T Lymphocytes: Balancing Quiescence and Activation
In the realm of CD4+ T lymphocytes, IL-15 takes on a dual role. While both IL-15 and IL-7 are essential for basal homeostatic proliferation under normal conditions, memory CD4+ T lymphocytes showcase less dependency on IL-15 compared to their CD8+ counterparts. IL-15’s impact on CD4+ T cell activation is contingent on TCR engagement, inducing quiescence in the absence of triggering but robust proliferation and resistance to TCR-induced cell death when concomitant engagement occurs. Intriguingly, IL-15 elevates CD154 expression on activated CD4+ T lymphocytes, enhancing their interaction with antigen-presenting cells.
Maintaining Equilibrium in Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Responses
IL-15’s influence extends beyond mere proliferation; it navigates the intricate landscape of regulatory T cells (Tregs). Notably, IL-15 prevents suppressive effects by natural Tregs, potentially unleashing transient pro-inflammatory responses against pathogens. Paradoxically, it also promotes the acquisition of regulatory functions by CD4+CD25− T cells. This delicate balancing act raises questions about the potential deleterious effects during chronic infections with prolonged IL-15 overexpression.
Aging and IL-15: A Fountain of Youth for Immune Vigor?
As the immune system ages, IL-15 steps in as a potential rejuvenator. Studies reveal that IL-15 preferentially stimulates the proliferation of CD4+CD28(null) T cells, enhancing their cytotoxic properties. This finding opens avenues for considering IL-15 as a stimulant for immune responses in the elderly, potentially countering the decline in immune efficacy associated with aging.
IL-15’s Role in B Lymphocytes: Co-stimulation and Beyond
Contrary to initial beliefs, IL-15 demonstrates its influence on B lymphocytes. While it may not directly stimulate resting B cells, IL-15 proves to be a potent co-stimulator in response to specific triggers. Notably, in conjunction with CD40 ligand, IL-15 induces substantial polyclonal IgM, IgG1, and IgA secretion, unveiling a nuanced role in shaping antibody responses.
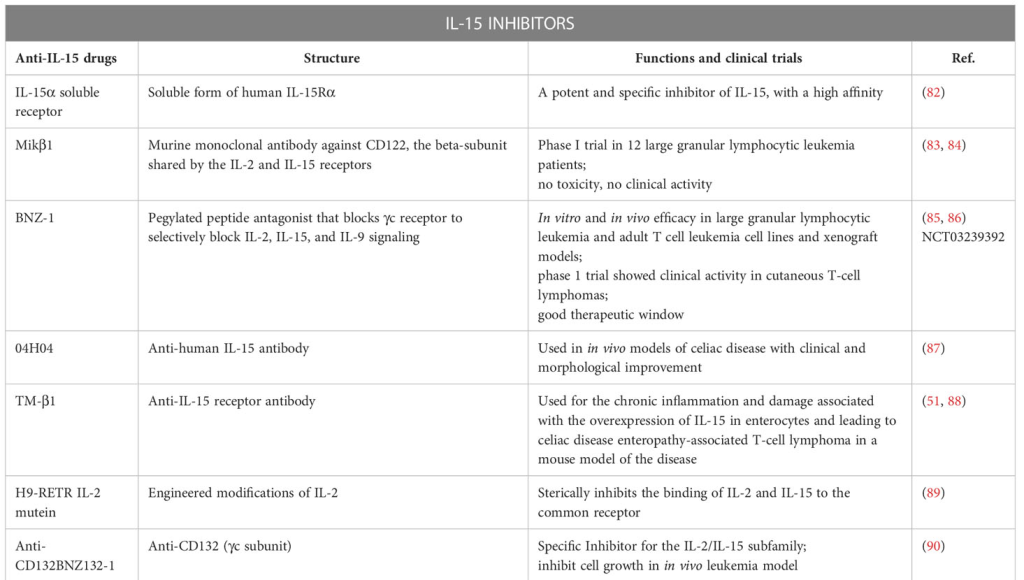
IL-15 in the Viral Realm: A Double-Edged Sword
HIV-1: From Activation to Protection
IL-15 emerges as a potential immunotherapeutic in HIV-1 infection. Studies reveal its ability to reverse functional impairment of NK cells, induce proliferation of CD4+ effector memory T lymphocytes, and potentially enhance the immune response. However, caution is warranted, as IL-15 might inadvertently increase viral replication during the acute phase.
HTLV-1: Implications for Neurological Disorders
IL-15’s involvement in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) becomes evident. Spontaneous proliferation of PBMCs in HAM/TSP patients, orchestrated by IL-15, underscores its potential therapeutic relevance in mitigating the impact of HTLV-1 infections.
Herpesviruses: A Guardian or Accomplice?
IL-15’s role in herpesvirus infections unfolds with its ability to enhance NK cell activity and control viral replication. Notably, IL-15’s impact on HSV-2 infections reveals a delicate balance, with potential complications arising from immune responses triggered by excess IL-15.
Hepatitis B and C Viruses: Navigating the Immune Landscape
IL-15’s role in hepatitis virus infections, particularly HBV and HCV, presents a complex scenario. While IL-15’s association with disease progression is implicated in chronic HCV infections, its role in acute HBV infections remains elusive, highlighting the need for nuanced understanding in viral contexts.
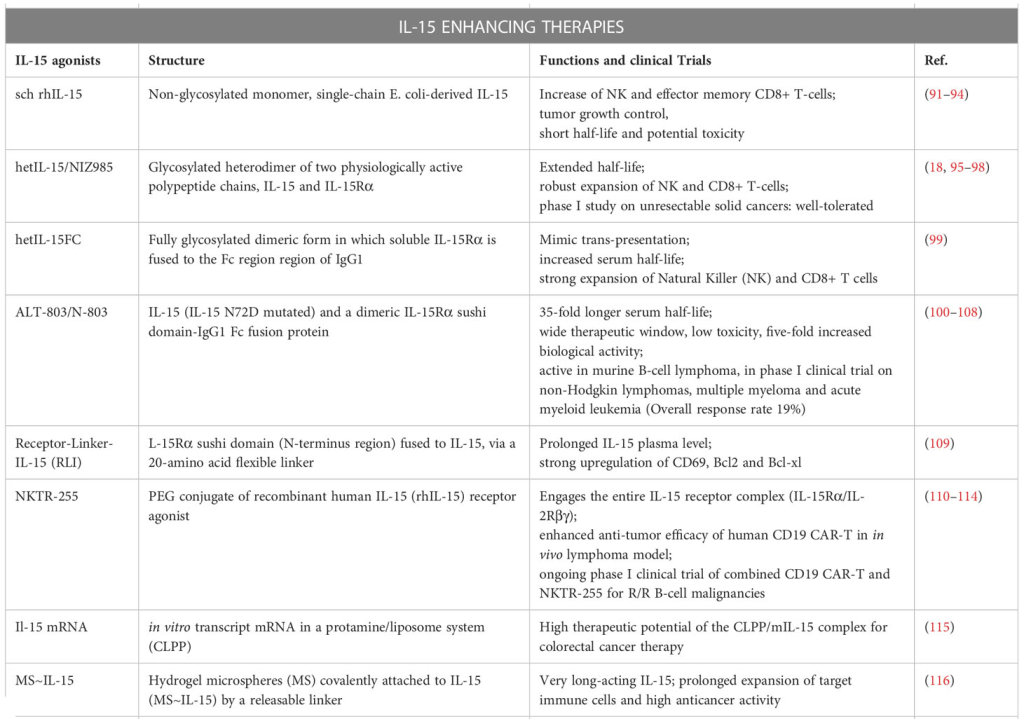
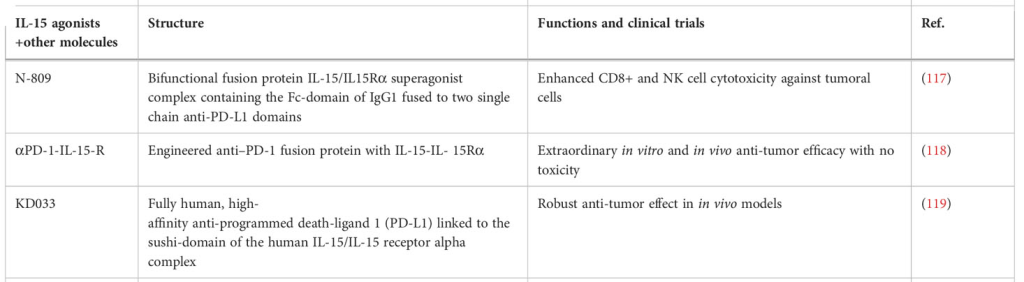
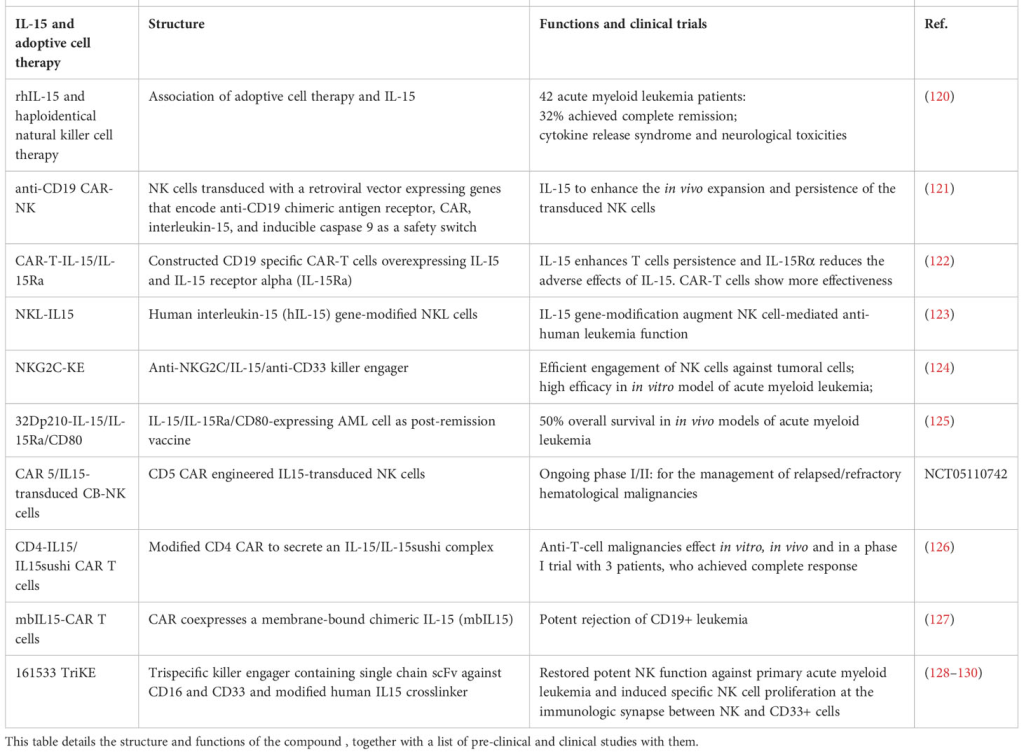
Eubacterial Dynamics and Beyond: IL-15’s Role in Bacterial and Parasitic Infections
M. tuberculosis and the Immunological Tapestry
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the insidious bacterium behind tuberculosis, unveils a host-pathogen symphony where immune responses form a spectrum rather than discrete phases. Innate immune warriors—macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), NK cells, and granulocytes—join forces to eliminate the intracellular foe. Adaptive immunity’s choreography involves CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, orchestrated by IFN-γ and TNF-α, alongside IL-17-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes. Notably, IL-15 emerges as a pivotal player, with studies in BALB/c mice hinting at its potential therapeutic role, particularly when administered post-infection. Paradoxically, IL-15’s protective image wavers as higher IL-15 levels correlate with active tuberculosis, posing intricate questions about its role in disease progression. Human studies further cloud the narrative, underscoring the challenge of pinpointing cause and effect amid variables like exposure time, bacterial strain, and co-infections.
A Cornucopia of Bacterial Melees
Beyond tuberculosis, IL-15’s saga unfolds in diverse bacterial battles. In Salmonella typhimurium infection, IL-15 and NK cells weave an innate shield against colonization, spotlighting IL-15’s pivotal role in gut and systemic defense. Conversely, IL-15’s dark side emerges in inflammatory bowel diseases, revealing its Janus-faced nature. Strikingly, IL-15 proves a potent ally in combatting sepsis, thwarting apoptosis, and orchestrating an immunostimulatory symphony. The enigma persists as IL-15’s protective veil shields against some bacterial foes but unravels vulnerabilities in others.
IL-15’s Versatility in Parasitic Duels
IL-15’s involvement extends beyond bacteria, entering the realm of parasitic warfare. From malaria to Toxoplasma gondii, IL-15 showcases its versatile role. In malaria, IL-15 orchestrates innate and adaptive defenses, while in Cryptosporidium infection, it empowers NK cells for intracellular elimination. However, the tale takes a twist in Toxoplasma gondii, where IL-15-induced memory CD8+ T lymphocytes falter, underscoring the nuanced interplay in parasitic combat. IL-15 emerges as a double-edged sword, wielding protection against some parasites while navigating complexities in others.
IL-15: Herald to a New Era of Prevention and Treatment
IL-15 as a Vaccine Adjuvant
In the quest for effective vaccines against diverse pathogens, IL-15 emerges as a conductor orchestrating robust immune responses. Its prowess as a vaccine adjuvant shines in studies against HIV, influenza, and tuberculosis, inducing enduring cellular and humoral immunity. Impressively, IL-15’s inclusion enhances protection in models ranging from Brucella abortus to Trypanosoma cruzi, promising a new era in vaccine development. Yet, IL-15’s melody is not without discord; it prompts erosion of pre-existing memory during infections, adding a complex note to its vaccine adjuvant symphony.
IL-15’s Prelude in Non-Human Primate Trials
As IL-15 inches closer to clinical application, insights from rhesus macaques offer a prelude. Intriguingly, clinical-grade recombinant human IL-15 proves safe, inducing an orchestrated expansion of immune cells without triggering IL-2-associated side effects. However, the melody shifts with glycosylated versus nonglycosylated IL-15, underscoring the need for meticulous evaluation. Current trials against metastatic malignant melanoma and renal cell cancer hold promise for IL-15’s future therapeutic crescendo.
The Immune Saga Continues
In conclusion, IL-15, recognized for its robust cytokine properties, emerges as a pivotal player in bolstering both innate and adaptive immune responses against pathogens. Its unique characteristics, distinct from IL-2, position it as a promising cytokine adjuvant for vaccine strategies, enhancing its efficacy in infectious disease defense. As we navigate the potential of IL-15 in immunotherapy, leveraging its ability to activate a spectrum of immune cells, it holds promise for addressing disorders and infections that can benefit from the heightened activities of these effector cell populations.
Study DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.10.006
Engr. Dex Marco Tiu Guibelondo, B.Sc. Pharm, R.Ph., B.Sc. CpE
Subscribe
to get our
LATEST NEWS
Related Posts

Immunology & Oncology
Degradation Code: Rewriting Pathology by Reprogramming Intracellular Protein Fate
Targeted protein degradation transforms pharmacology from inhibition to elimination, redefining how we therapeutically control protein-driven disease.

Immunology & Oncology
Signal Switch: Stimuli-Responsive Nanoplatforms That Turn STING On Only Where Tumors Make Sense
Stimuli-responsive STING nanomedicine is an effort to make innate immune activation behave like a gated, tumor-local event rather than a body-wide inflammatory signal.

Immunology & Oncology
Marrow Whispers: How B-Cell Circuitry May Shape Acquired Aplastic Anemia and Why CD20 Depletion Is Being Reconsidered
Acquired aplastic anemia may sometimes be maintained by B-cell–supported immune networks, making CD20 depletion a biologically coherent but still nonstandard therapeutic hypothesis.
Read More Articles
Algorithmic Therapeutics: Artificial Intelligence Reshaping Biotech Drug Discovery and Product Development
Artificial intelligence is transforming biotech by making therapeutic discovery less like screening for luck and more like engineering across molecules, biologics, and delivery systems.
Factory Logic: Modular Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Enabling Rapid Drug Production and Continuous Innovation
Modular pharmaceutical factories transform drug manufacturing into a continuously evolving technological system capable of integrating new therapies, processes, and production innovations without disrupting regulated operations.
Spatial Collapse: Pharmacologic Degradation of PDEδ to Disrupt Oncogenic KRAS Membrane Localization
PDEδ degradation disrupts KRAS membrane localization to collapse oncogenic signaling through spatial pharmacology rather than direct enzymatic inhibition.
Neumedics’ Integrated Innovation Model: Dr. Mark Nelson on Translating Drug Discovery into API Synthesis
Dr. Mark Nelson of Neumedics outlines how integrating medicinal chemistry with scalable API synthesis from the earliest design stages defines the next evolution of pharmaceutical development.
Zentalis Pharmaceuticals’ Clinical Strategy Architecture: Dr. Stalder on Data Foresight and Oncology Execution
Dr. Joseph Stalder of Zentalis Pharmaceuticals examines how predictive data integration and disciplined program governance are redefining the future of late-stage oncology development.