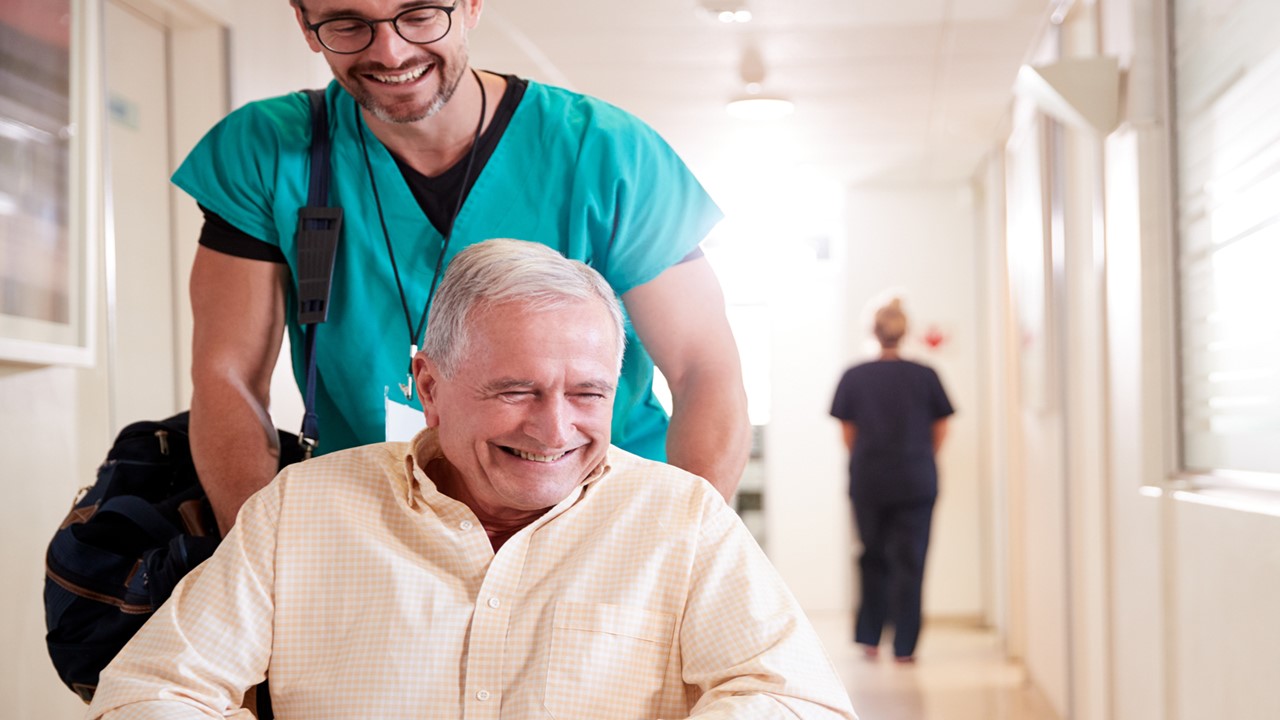
A delicate balance between public and private investments shapes the pharmaceutical research and development (R&D) landscape. While governments historically played a significant role in funding R&D, a notable shift towards private sector dominance has occurred since the 1980s. This trend is evident across major industrialized nations and OECD countries, where the private sector now accounts for a substantial portion of total national R&D expenditure.
Despite this, a symbiotic relationship persists between public institutions and private firms, particularly in the discovery and development of groundbreaking drugs. Notably, public funding has played a pivotal role in spearheading key drug discoveries, ranging from treatments for infectious diseases to antiretrovirals for HIV/AIDS. The collaboration between publicly funded research institutions and the private pharmaceutical industry underscores the crucial interdependence of both sectors in driving innovation and advancing therapeutic interventions.
Navigating the Complex Terrain of Pharmaceutical Innovation
Innovation within the pharmaceutical industry has undergone a profound evolution, transitioning from models centered on absolute novelty to ones driven by the routine exploitation of existing technologies. This shift has led to a cumulative model of innovation, where incremental improvements and “me too” drugs dominate the landscape. While these developments have fueled the proliferation of pharmaceutical products, concerns regarding patent quality and strategic patenting practices have come to the forefront.
Originally designed to reward inventions of considerable originality, the patent system is now inundated with grants covering minor and incremental developments. Consequently, this trend not only stifles genuine innovation but also erects barriers to entry, hindering competition and impeding access to affordable medicines. Addressing these challenges will be paramount in fostering a more equitable and sustainable framework for pharmaceutical innovation, ensuring that the benefits of scientific progress are accessible to all.

Towards a Sustainable Future for Pharmaceutical Innovation
In charting the course for the future of pharmaceutical innovation, stakeholders must prioritize collaborative efforts aimed at promoting transparency and accountability in patent procurement and enforcement. By fostering an environment conducive to open innovation and knowledge sharing, the industry can harness the collective expertise of diverse stakeholders to drive meaningful advances in drug discovery and development. Additionally, policymakers must adopt measures to strengthen patent standards and curb the proliferation of low-quality patents that serve as barriers to innovation.
Embracing a holistic approach that balances the interests of public health with those of industry stakeholders will be essential in realizing the full potential of pharmaceutical innovation to address pressing global health challenges.
Empowering Emerging Economies in Pharmaceutical Innovation
Furthermore, efforts to enhance access to medicines must extend beyond traditional markets to include emerging economies, where access barriers persist due to a combination of economic, regulatory, and intellectual property-related challenges. By leveraging innovative financing mechanisms and technology transfer initiatives, developed nations can support the capacity-building efforts of emerging economies, enabling them to participate more actively in pharmaceutical R&D and expand access to essential medicines for their populations. This collaborative approach not only promotes global health equity but also fosters a more inclusive and sustainable model of pharmaceutical innovation that benefits people worldwide.
Study DOI: 10.1038/nrd3078-c1
Article Banner Credits: Xavier Becerra speaks during a news conference on June 28. Photo: Amanda Andrade-Rhoades/Bloomberg via Getty Images.
Engr. Dex Marco Tiu Guibelondo, B.Sc. Pharm, R.Ph., B.Sc. CpE
Subscribe
to get our
LATEST NEWS
Related Posts

Clinical Operations
Beyond the Intervention: Deconstructing the Science of Healthcare Improvement
Improvement science is not a discipline in search of purity. It is a field forged in the crucible of complexity.

Clinical Operations
Translating Innovation into Practice: The Silent Legal Forces Behind Clinical Quality Reform
As public health increasingly intersects with clinical care, the ability to scale proven interventions becomes a core competency.
Read More Articles
Myosin’s Molecular Toggle: How Dimerization of the Globular Tail Domain Controls the Motor Function of Myo5a
Myo5a exists in either an inhibited, triangulated rest or an extended, motile activation, each conformation dictated by the interplay between the GTD and its surroundings.
Designing Better Sugar Stoppers: Engineering Selective α-Glucosidase Inhibitors via Fragment-Based Dynamic Chemistry
One of the most pressing challenges in anti-diabetic therapy is reducing the unpleasant and often debilitating gastrointestinal side effects that accompany α-amylase inhibition.