The landscape for rare pediatric diseases has long been overshadowed by the success stories of treatments for common adult conditions. However, a Florida-based radiopharmaceutical company, Advanced Innovative Partners (AIP), is venturing into uncharted territories, determined to bridge the gap for the thousands of children grappling with rare and often overlooked illnesses.
The Orphaned Battle: AIP’s Mission in Rare Pediatric Diseases
A rare or orphan disease is characterized by its low prevalence, affecting less than 6.5–10 cases in 10,000 people. The National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) and Orphanet are dedicated organizations working towards the betterment of individuals grappling with such rare conditions. Orphan drugs, designed for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of these orphan diseases, play a pivotal role in addressing the unique healthcare needs of this underserved population.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) actively contributes to the field by maintaining a comprehensive list of orphan drug designations and approvals. Within this realm, partial orphan drugs emerge, showcasing dual indications—serving both orphan and non-orphan purposes.
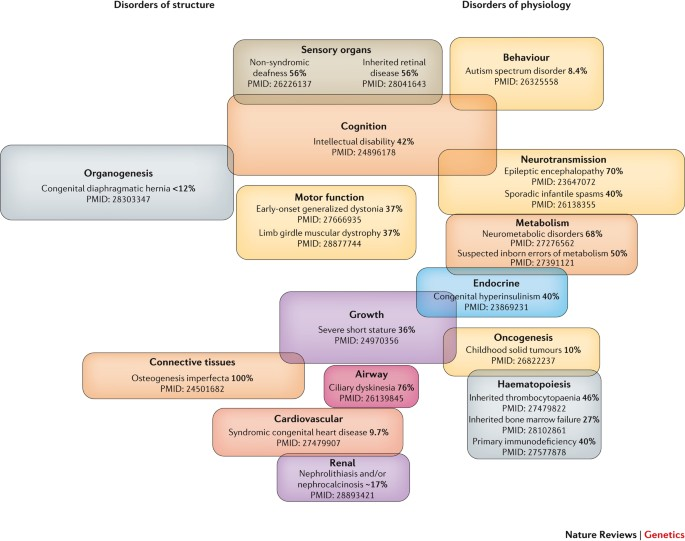
So far, a staggering 7,000 rare pediatric diseases have been identified, yet a mere 5% boast FDA-approved pharmacotherapies. The term “orphan diseases” aptly characterizes these conditions, as the small patient populations render them commercially unattractive to pharmaceutical giants. This unfortunate reality translates into a lack of viable treatments, leaving afflicted children to contend with debilitating symptoms and truncated life expectancies.
In response to this unmet need, AIP has positioned itself as a pioneer, harnessing its expertise in radiochemistry and drug development to craft a beacon of hope for families navigating the tumultuous waters of rare pediatric diseases. Dr. Stanley “Stan” Satz, Co-Founder, Chairman & Chief Scientific Officer of AIP, underscores the promise of radiopharmaceuticals in this domain, stating, “Radiopharmaceuticals are ideally suited for rare disease applications as they can selectively deliver radiation payloads directly to organs of interest.”
Precision Beyond Measure: AIP’S Radiopharmaceutical Arsenal
AIP’s arsenal is built upon the strategic use of radioisotopes, including lutetium-177, copper-64, and gallium-68. These elements form the crux of diagnostic scans and treatments that hold the potential to revolutionize the landscape of rare pediatric diseases. By employing precision-targeted radiomedicines, AIP aims to unleash a profound impact on the lives of children grappling with these devastating conditions.
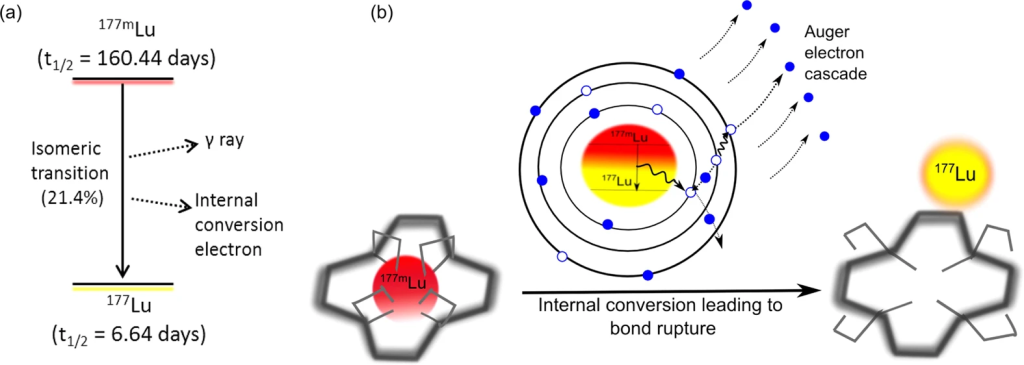
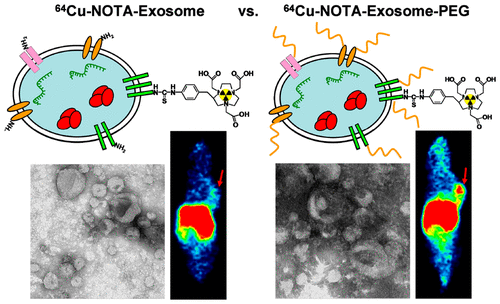

Targeting the Unseen Enemy: AIP’s Focus on Neuroendocrine Cancers
Among the array of rare pediatric diseases, AIP has zeroed in on the challenging terrain of rare neuroendocrine cancers, such as pheochromocytoma. Afflicting approximately 300 pediatric patients annually in the United States, these cancers demand innovative solutions.
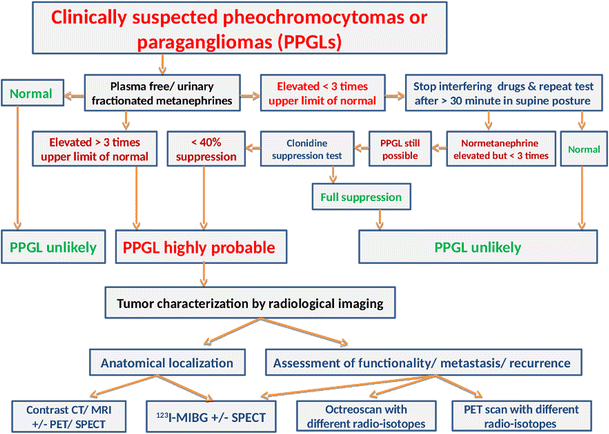
Pheochromocytomas and Hypertension. Current Hypertension Reports 20(1). doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0804-z.
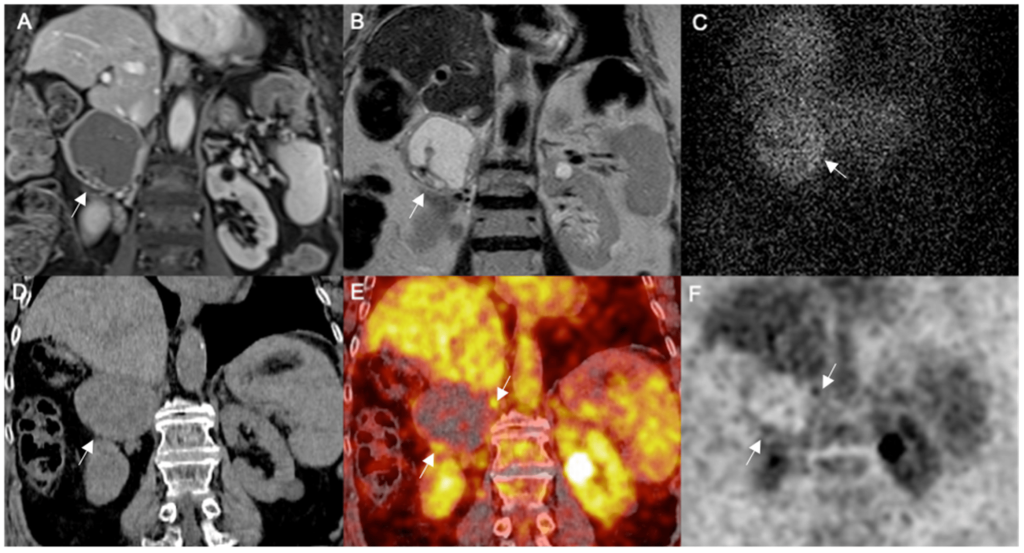
AIP’s foray into peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) represents a promising avenue, honing in on receptors overexpressed on tumor cells to deliver targeted radiation. Check out this AIP – PRRT article for more details.
Navigating Unchartered Waters: AIP Explores Rare Metabolic Disorders
Beyond cancer, AIP is navigating uncharted waters in the realm of rare metabolic disorders. Wilson disease, characterized by toxic copper accumulation in the liver and brain, presents a formidable challenge.

AIP envisions a solution through copper-64 labeled agents, enabling both imaging and treatment. While the business case is undeniably challenging, AIP Co-Founder, CEO & President Roseanne “Rose” Satz, asserts the company’s commitment, stating, “For children and families afflicted with these conditions, new safe and effective therapies are nothing short of life-changing.”
AIP’s Radiopharmaceutical Symphony: A Creative Overture in Pediatric Medicine
AIP’s creative approach to radiopharmaceutical research and development emerges as a distinctive and harmonious melody in the grand symphony of pediatric medicine. The company’s unwavering commitment to innovation embodies the spirit of hope and progress, promising a brighter future for the countless children whose lives hang in the balance of groundbreaking treatments. As AIP takes center stage, it beckons a new era in pediatric medicine—one where precision and compassion converge to reshape the narrative of rare pediatric diseases.
About Advanced Innovative Partners (AIP)
Advanced Innovative Partners (AIP) emerges as a prominent global clinical-stage biotechnology company, standing at the forefront of diagnostic and therapeutic advancements in the realm of targeted radiation. Founded in 2017, AIP boasts a skilled team with expertise spanning biotechnology, nuclear medicine, and molecular biology. Their commitment lies in the development of next-generation diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals, addressing critical needs in oncology, rare pediatric diseases, infectious diseases, and biomedical countermeasures.

At the heart of AIP’s operations is a robust pipeline, extending its reach to breast, lung, brain, and solid tumor cancers, as well as rare diseases. AIP navigates this expansive landscape with a reliable, secure global supply chain and a collaborative network, ensuring the seamless progression of their innovative products from development to delivery.
With lead programs advancing through Phase I/II/III clinical trials, AIP positions itself as a leader in the emerging market space of radiopharmaceutical diagnostics and therapeutics. The company’s success is underpinned by patented platform technologies that underscore their commitment to excellence in treatment and clinical management. AIP’s approach is product-centric, reflected in the creation of a pipeline comprising multiple drugs strategically targeting areas with significant market opportunities.
AIP’s mission revolves around expediting the discovery, development, and global availability of transformative therapies. Their focus extends beyond innovation, emphasizing the importance of rigorous clinical trials mandated by regulatory bodies. By navigating these regulatory pathways and obtaining approvals, AIP aims to make their investigational products accessible to patients worldwide.
Central to AIP’s identity is a dedication to pioneering targeted therapies and advancing disease detection and treatment. This commitment unfolds through a comprehensive, integrated approach encompassing proprietary tech platforms, strategic partnerships, and an unwavering patient-centric focus. AIP’s ultimate goal is to profoundly impact patient journeys by enabling accurate diagnoses at an earlier stage and providing treatments that are not only more powerful but also gentler, thereby offering patients the best chance for improved outcomes. In essence, AIP aspires to make a meaningful difference for individuals grappling with complex, aggressive, rare, and infectious diseases worldwide.

Learn more about AIP from their Official Website.
Engr. Dex Marco Tiu Guibelondo, B.Sc. Pharm, R.Ph., B.Sc. CpE
Subscribe
to get our
LATEST NEWS
Related Posts

Medicinal Chemistry & Pharmacology
Synthetic Chemistry’s Potential in Deciphering Antimicrobial Peptides
The saga of antimicrobial peptides unfolds as a testament to scientific ingenuity and therapeutic resilience.
Medicinal Chemistry & Pharmacology
Appreciating the Therapeutic Versatility of the Adenine Scaffold: From Biological Signaling to Disease Treatment
Researchers are utilizing adenine analogs to create potent inhibitors and agonists, targeting vital cellular pathways from cancer to infectious diseases.

Medicinal Chemistry & Pharmacology
The Potential of Benzazepine Derivatives: A Novel Eco-Friendly Synthesis Approach
Benzazepine derivatives, notable seven-membered heterocycles, have gained pharmaceutical interest for their diverse bioactive properties.
Medicinal Chemistry & Pharmacology
Bioavailability and Bioequivalence: The Makings of Similar and “Close Enough” Drug Formulations
Scientists are striving to understand bioavailability complexities to ensure the equivalence of drug formulations from different manufacturers, crucial for clinical effectiveness.