When it comes to developing new drugs, researchers encounter a formidable challenge: the prevalence problem. In the quest for pharmaceutical breakthroughs, scientists must navigate through a vast sea of potential compounds, where only a minuscule fraction will emerge as safe and effective treatments. This challenge is exacerbated by the rarity of both the desired therapeutic effects and the adverse reactions associated with experimental drugs.
Despite employing meticulous laboratory tests and extensive clinical trials, detecting these rare events remains elusive. The prevalence problem not only prolongs the drug development process but also incurs substantial costs. Thus, innovative approaches and rigorous statistical methodologies are indispensable in addressing this pervasive issue.
The Black Swan Phenomenon
The concept of “black swan events,” as elucidated by Nassim Nicholas Taleb, aptly characterizes the rarity and consequential impact of certain occurrences, such as those encountered in drug discovery. Taleb is a Lebanese-American writer, mathematical statistician, former trader in options, risk analyst, and creator of aphorisms. His body of work revolves around topics related to randomness, probability, and uncertainty. The Sunday Times called his 2007 book The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable one of the 12 most influential books since World War II.

Just as black swans defy conventional expectations, truly efficacious drugs and unforeseen toxicities emerge unexpectedly, reshaping the landscape of pharmaceutical development. Taleb’s insights underscore the inherent uncertainty and complexity inherent in identifying rare yet significant events, necessitating a paradigm shift in predictive methodologies.
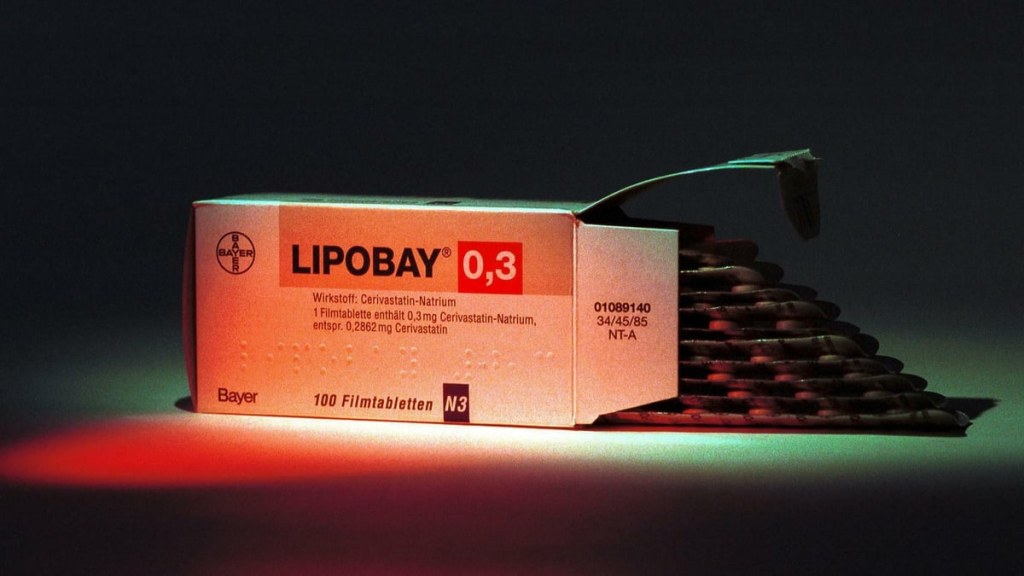
The Curious Cases of Vioxx & Lipobay
The cautionary tales of COX-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) Vioxx (rofecoxib) and the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor Lipobay (cerivastatin) epitomize the challenges posed by the prevalence problem in drug discovery. Initially lauded for their therapeutic potential, these drugs were later marred by unforeseen adverse effects, including cardiovascular complications and severe muscle toxicity, respectively. Despite rigorous testing protocols, these rare but impactful events eluded early detection, underscoring the imperative of more sensitive and comprehensive evaluation methods.

Challenges in Identifying Rare Events
The prevalence problem is further compounded by the inherent limitations of testing methodologies, particularly in distinguishing true positives from false signals amidst vast pools of candidate compounds. Statistical analyses reveal the diminishing returns and escalating risks associated with identifying rare but valuable drug candidates. Despite advancements in testing technologies, the probabilistic nature of drug discovery necessitates a nuanced understanding of the inherent uncertainties.


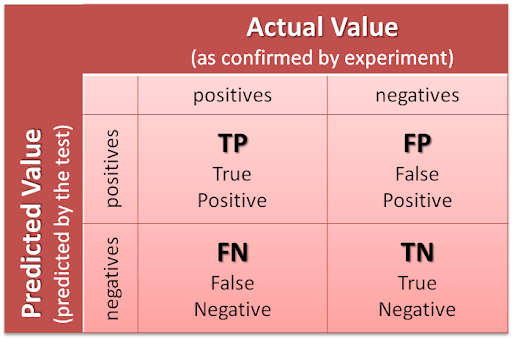
Strategies for Improvement: Enhancing Predictive Models
In light of these challenges, several strategies emerge to enhance the predictive capacity of drug discovery processes. Embracing high-throughput screening methods, leveraging multi-parameter testing approaches, and integrating supplementary data sources represent promising avenues for improving the efficiency and accuracy of candidate selection. Furthermore, the advent of human-relevant bioengineered models and big-data-driven analyses holds immense potential in mitigating the prevalence problem.
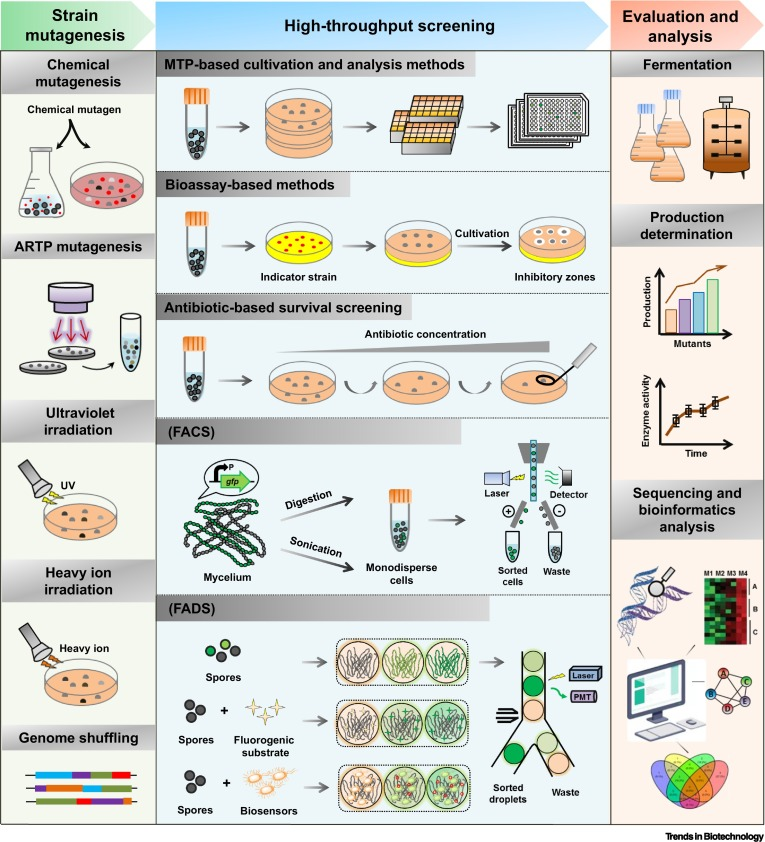
Balancing Tradition and Innovation
The pharmaceutical industry occupies a unique position in its reliance on animal testing while concurrently driving innovation in alternative methodologies. Despite stringent regulatory requirements and lengthy development cycles, pharmaceutical companies are at the forefront of adopting novel technologies to enhance safety testing and accelerate drug development. Through a combination of market incentives, regulatory flexibility, and scientific innovation, the industry endeavors to overcome the prevalence problem and usher in a new era of pharmaceutical discovery.
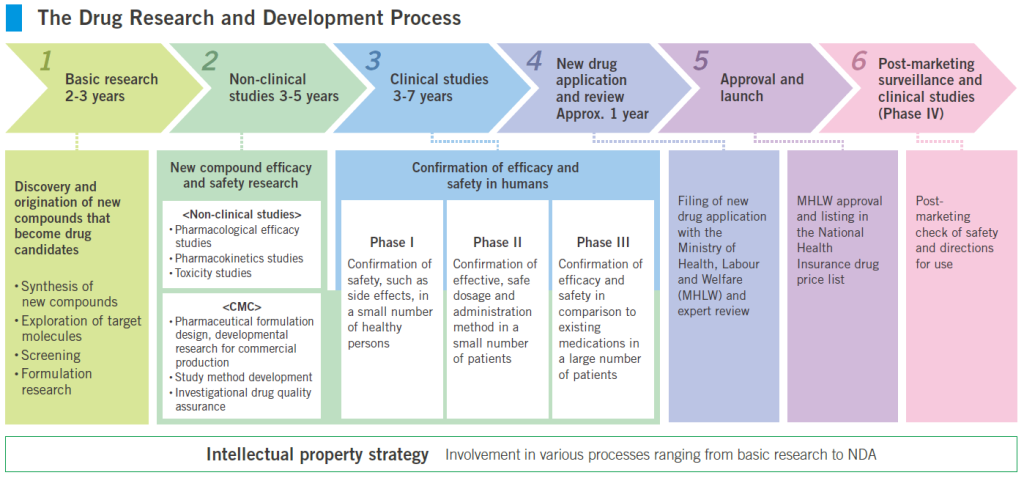
Charting a Course Forward
As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, navigating the prevalence problem remains a formidable yet surmountable challenge. By embracing innovative approaches, leveraging predictive models, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, researchers can illuminate the path towards more efficient and effective drug discovery.
While the prevalence problem may persist as an inherent aspect of pharmaceutical research, it is through resilience, ingenuity, and unwavering commitment that scientists will ultimately unravel the mysteries of drug development and forge new frontiers in healthcare.
Engr. Dex Marco Tiu Guibelondo, B.Sc. Pharm, R.Ph., B.Sc. CpE
Editor-in-Chief, PharmaFEATURES

Subscribe
to get our
LATEST NEWS
Related Posts
Molecular Biology & Biotechnology
Myosin’s Molecular Toggle: How Dimerization of the Globular Tail Domain Controls the Motor Function of Myo5a
Myo5a exists in either an inhibited, triangulated rest or an extended, motile activation, each conformation dictated by the interplay between the GTD and its surroundings.

Drug Discovery Biology
Unlocking GPCR Mysteries: How Surface Plasmon Resonance Fragment Screening Revolutionizes Drug Discovery for Membrane Proteins
Surface plasmon resonance has emerged as a cornerstone of fragment-based drug discovery, particularly for GPCRs.
Read More Articles
Designing Better Sugar Stoppers: Engineering Selective α-Glucosidase Inhibitors via Fragment-Based Dynamic Chemistry
One of the most pressing challenges in anti-diabetic therapy is reducing the unpleasant and often debilitating gastrointestinal side effects that accompany α-amylase inhibition.